In this article we will talk about RESTful API development and architecture.
WHAT IS A RESTful API?
- API stands for Application Programmable Interface which is a way computer programs communicate with each other.
- APIs provide a standard for sharing data, performing tasks and extending functionality of a system.
- APIs abstract implementation of functionality to the developers consuming (integrating into) them.
WEB API
- Web APIs sit between the application and the web server and perform tasks on requests called API calls.
- When a user initiates a request the application will use an API (make an API call) requesting the web server to perform that task.
REST API
- REpresentational State Transfer is an API architectural style that makes it easy for computer systems to communicate with the web.
- It uses HTTP requests to access and perform actions on resources and data on web servers.
WHY RESTful API?
- REST can support multiple formats for storing and exchanging data. A response can be in XML, JSON, HTML and Plain text format.
- It allows for caching of data on the HTTP Level. This caching of data provides better system performance.
- It abstracts functionalities allowing for easy integration into existing systems. Developers can easily add different APIs and API functionalities without rewriting the system every time.
RESTful API ARCHITECTURE

A user interacts with an API through a user interface on a client:
Client can be a laptop, a tablet or mobile phone.
The API is hosted on a server which is accessed over a network, commonly the internet, using the HTTP protocol using action verbs.
Action verbs specify an action to be performed on a specific resource or a collection of resources.
POST: The POST verb is most-often utilized to create new resources
PUT: PUT is most-often utilized for update capabilities. The old existing resource is completely replaced by the object in the body of a PUT request.
DELETE: DELETE is pretty easy to understand. It is used to delete a resource.
PATCH: PATCH is used for modify capabilities. The PATCH request only needs to contain the changes to the resource, not the complete resource.
GET: The HTTP GET method is used to read (or retrieve) a representation of a resource.
When a Request is made by the client, it sends this information in the HTTP request.
After performing the specified action, the API then responds to the client with a Response that the application formats to a user friendly view which is most commonly a JSON object.
JSON
- JSON stands for JavaScript Object Notation, which is a lightweight data-interchange format.
- JSON facilitates sending data between computers systems. It is easy to work with data as JavaScript objects, with no complicated parsing and translations.
- JSON can receive pure text from a server and use it as a JavaScript object.
- JSON can also send a JavaScript object to a server in pure text format.
JSON OBJECT
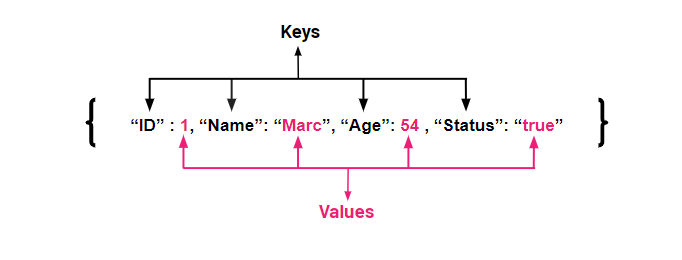
- JSON Objects are surrounded by curly braces.
- They are written in key/value pairs.
- Keys must be strings and values must be valid JSON data types: string, number, another JSON object, array, boolean or null.
Hopefully you know have a better understanding about RESTful APIs. Make sure to also check out our article about Dependency Injection.


